Poor Sleep and Gut Health? These 2 Supplements Work for Both
Introduction
Tossing and turning at night while your stomach feels off? You’re not alone. The connection between sleep and gut health is more powerful than most people realize—when one suffers, the other often suffers as well. Poor sleep can disrupt your gut microbiome, while an unhealthy gut can make quality sleep nearly impossible. It’s a frustrating cycle that leaves you exhausted and uncomfortable. The good news? Two evidence-based supplements—probiotics and omega-3 fatty acids—can address both issues simultaneously. Instead of treating your sleep problems and gut issues separately, these nutrients work together to restore balance in your body. Let’s explore how strengthening your gut bacteria and sleep patterns with the right supplements can transform your overall health and finally break this exhausting cycle.
- Why sleep and gut health affect each other
- How probiotics and omega-3s may help (and what the research actually says)
- General guidance on dosages used in studies
This isn’t about perfection. It’s about understanding your options and finding what might work for you.
Ready to Break the Sleep-Gut Cycle?
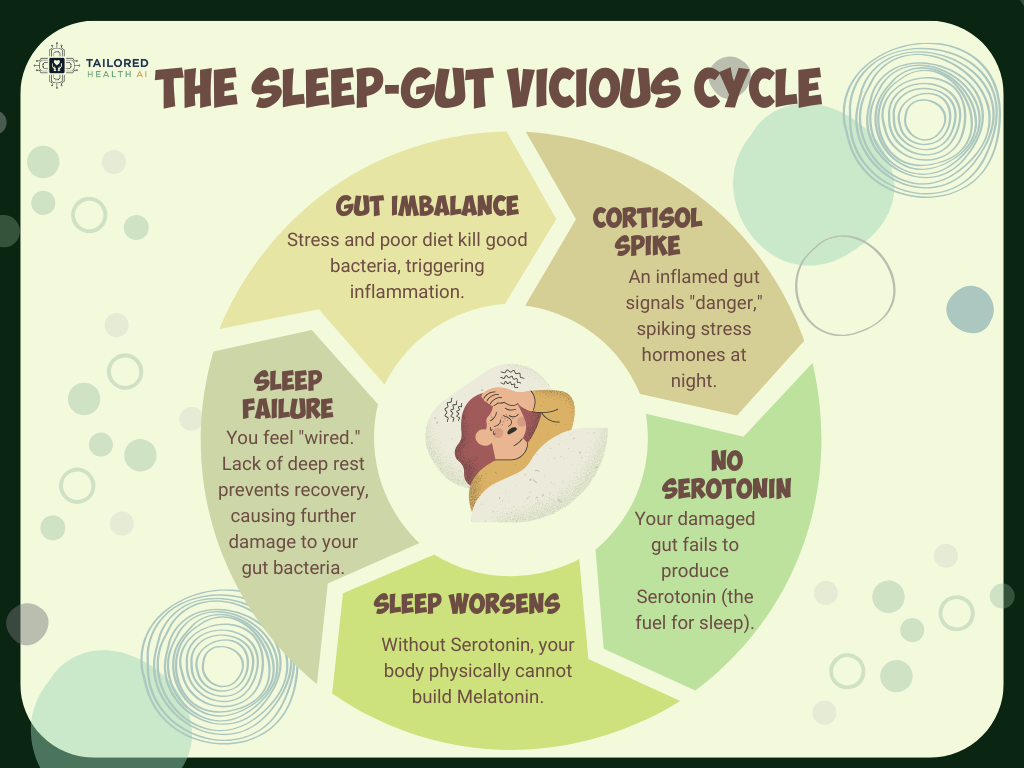
How Poor Sleep Damages Your Gut
| Sleep Issue | Impact on Gut |
|---|---|
| Less than 7 hours sleep | Reduces beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium |
| Irregular sleep schedule | Disrupts gut microbiome diversity. |
| Sleep deprivation | Sleep deprivation |
| Poor sleep quality | Triggers gut inflammation and reduces short-chain fatty acid production |
How Poor Gut Health Disrupts Your Sleep:
| Gut Problem | Sleep Impact |
|---|---|
| Low microbial diversity | Reduces sleep efficiency and increases nighttime awakenings |
| Gut inflammation | Interferes with melatonin production (your sleep hormone) |
| Imbalanced gut bacteria | Decreases GABA production, making it harder to fall asleep |
| Poor gut health | Lowers serotonin levels (90% is made in your gut), affecting sleep regulation |
The key player?
Your gut microbiome produces neurotransmitters and hormones that directly control your sleep-wake cycle, while your sleep quality determines which bacteria thrive in your digestive system.
Probiotics for Gut and Sleep
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that restore balance to your gut microbiome—and emerging research shows they’re powerful sleep aids too.
How Probiotics Improve Both Gut Health & Sleep
- Boost GABA production – Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains produce gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that calms your nervous system and promotes deeper sleep (Cleveland Clinic)
- Reduce cortisol levels – Probiotics lower stress hormone cortisol by up to 32%, helping you fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer (NIH)
- Strengthen gut barrier – They repair intestinal lining, reducing inflammation that disrupts sleep cycles (National Institutes of Health)
- Increase serotonin synthesis – Enhanced gut health means more serotonin production, which converts to melatonin at night (Johns Hopkins Medicine)
Best Probiotic Strains for Sleep and Gut Health
| Strain | Gut Benefit | Sleep Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus | Reduces gut inflammation, improves digestion | Decreases anxiety, improves sleep quality |
| Bifidobacterium longum | Strengthens intestinal barrier, balances microbiome | Reduces cortisol, enhances REM sleep |
| Lactobacillus plantarum | Supports nutrient absorption, reduces bloating | Increases sleep duration and efficiency |
| Bifidobacterium breve | Alleviates IBS symptoms, boosts immunity | Improves overall sleep satisfaction scores |
Recommended Dosage
What the Research Shows
Clinical studies on probiotics for sleep and gut health typically use dosages ranging from 10 to 20 billion CFUs per day, taken with food. (Mayo Clinic).
Important to know:
- Research shows benefits across different dosage levels
- Some people respond to lower amounts, others to higher
- Strain type often matters as much as dosage
- Individual response varies—what works for your friend might not work the same way for you
⚠️ Consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen, especially if you have existing health conditions or take medications. These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA. Probiotics are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Clinical Evidence:
A 2023 study found that participants taking multi-strain probiotics for 8 weeks experienced 67% improvement in sleep quality and a significant reduction in digestive discomfort (NIH). Researchers also noted improvements in sleep onset latency, with participants falling asleep an average of 15 minutes faster. Additionally, gut microbiome analysis showed increased populations of beneficial Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus species, which directly correlated with better sleep scores.
Not sure which probiotic strain is right for you?
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Essential Nutrients for Gut Healing and Deeper Sleep
Omega-3 fatty acids—particularly EPA and DHA—are powerful anti-inflammatory compounds that simultaneously heal your gut lining and regulate your sleep-wake cycle.
How Omega-3s Improve Both Sleep And Gut Health
- Reduce gut inflammation – EPA and DHA lower inflammatory markers in the intestinal tract by up to 58%, promoting faster gut healing (NIH)
- Enhance melatonin production – DHA increases melatonin synthesis, helping you fall asleep faster and maintain consistent sleep patterns (Performance Lab)
- Strengthen gut barrier – Omega-3s increase beneficial gut bacteria diversity and reduce intestinal permeability (NIH)
- Regulate circadian rhythm – DHA helps synchronize your body’s internal clock, improving both sleep quality and digestive function timing (Science Direct)
Omega-3 Benefits Breakdown
| Omega-3 Type | Impact on Gut | Impact on Sleep |
|---|---|---|
| EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid) | Reduces intestinal inflammation, heals gut lining | Decreases sleep-disrupting inflammation markers. |
| DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) | Supports gut barrier integrity, increases beneficial bacteria | Boosts melatonin, improves REM sleep duration by 58 minutes |
| ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid) | Promotes healthy gut microbiome diversity | Converts to EPA/DHA for indirect sleep benefits |
Recommended Dosage
What the Research Shows
Studies on omega-3s for sleep and gut health typically use dosages between 1,000 and 2,000mg of combined EPA and DHA per day, taken with meals.
Important to know:
- Different studies show benefits at different dosage levels
- Some research focuses more on EPA, some on DHA—both may be beneficial
- Quality of the supplement matters as much as the dose
- Like probiotics, individual response varies
⚠️ Consult your healthcare provider before starting omega-3 supplementation, especially if you take blood thinners or have bleeding disorders. These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA. Omega-3 supplements are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Clinical Evidence:
A recent review highlights that not all Omega-3s are equal when it comes to rest. The research found that DHA-rich supplementation successfully improved sleep quality in healthy adults, whereas EPA-heavy interventions showed little effect in specific clinical groups. According to a 2023 study published on PubMed, fish oil supplementation improved sleep quality in people with type 2 diabetes and was linked to increased activity in key circadian clock genes that help regulate the body’s internal clock.
The Synergistic Effect: Why They Work Better Together
Taking Probiotics and Omega-3s at the same time may combine their individual benefits, potentially supporting overall health in ways not seen when each is used alone. Emerging research suggests that Omega-3 fatty acids create an ideal environment for probiotics to colonize, while probiotics maximize the absorption of healthy fats. (NIH)
This section explains why taking both supplements creates a better result than taking just one.

What the Research Shows About Timing:
1. Probiotic studies often administer supplements with meals, as food may improve bacterial survival.
2. Omega-3 research typically includes supplementation with fat-containing meals, which may enhance absorption. Clinical trials emphasize consistent daily use over specific timing.
What Research Has Observed:
• Some studies report gut-related changes within 2-4 weeks of consistent use
• Sleep quality improvements in clinical trials often emerge around 4-8 weeks
• Individual response varies significantly—some people respond sooner, some later, some differently
Your experience may not match clinical trial averages.
| Synergy Factor | How They Interact | The Result |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Bacteria Survival | Omega-3 fats act as food for probiotics, helping the good bacteria survive and multiply in your gut. | The probiotic supplement becomes more effective because more bacteria survive. |
| Better Brain Communication | Probiotics create sleep chemicals (Butyrate); Omega-3s help transport these chemicals to the brain. | Your brain receives clearer signals to “shut down” for sleep. |
| Lowering Body Inflammation | Probiotics remove bad bacteria; Omega-3s block inflammation signals. | Stops “micro-awakenings” caused by physical stress and inflammation. |
| Boosting Sleep Hormones | Probiotics create Tryptophan; Omega-3s help your brain receptors use it. | Enhanced gut health means more serotonin production, which your body converts into melatonin at night. |
Stop Settling for Restless Nights and Digestive Discomfort
FAQs: Your Common Questions Answered Here
1. Taking probiotics with your evening meal
2. Including fermented foods in your diet regularly
3. Staying hydrated throughout the day (not chugging water right before bed)
4. A short walk after dinner — even 10-15 minutes
Important to know:
1. Different studies show benefits at different dosage levels
2. Individual response varies significantly
3. Quality and form of omega-3 supplements differ
4. Research participants typically take omega-3s with meals for better absorption
For your gut, studies link omega-3s to less inflammation, better intestinal barrier function, and more diverse beneficial bacteria. For sleep, they’re associated with better melatonin production and circadian rhythm support. One clinical study found DHA specifically increased REM sleep duration by nearly an hour.
⚠️Important Information
This article is for educational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice.
The information about supplements and health should not replace consultation with a qualified healthcare provider. Always consult your doctor before starting any new supplement, especially if you have existing health conditions, take medications, are pregnant, or are nursing.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. The supplements discussed are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Individual results vary significantly. What works for others may not work the same way for you.
